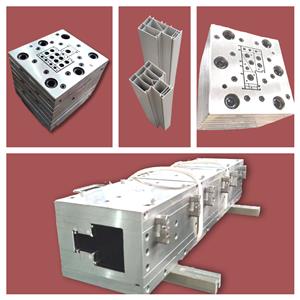
Plastik PVC, konstruksi cetakan ekstrusi, menyingkap tabir untuk Anda
Ada dua bentuk cetakan yang umum digunakan: cetakan berundak pelat dan cetakan gradien penampang. Jalur aliran cetakan berundak pelat berubah secara bertahap, yang terbuat dari beberapa templat mulut yang dihubungkan secara seri. Setiap pelat dikerjakan menjadi bentuk kontur yang sesuai, yang secara bertahap berubah dari bentuk saluran masuk yang bulat ke bentuk saluran keluar yang diinginkan. Ada bevel di pintu masuk setiap blok untuk menyelesaikan transisi dari satu bentuk ke bentuk lainnya. Biaya pemrosesan cetakan semacam ini rendah, saluran alirannya tidak ideal dan efisien, dan umumnya tidak perlu digunakan sebagai profil utama. Pelari cetakan gradien bagian disederhanakan, tidak ada zona retensi material di pelari, lelehan didistribusikan secara bertahap dan akurat ke setiap bagian bentuk saluran keluar dari lingkaran di saluran masuk, dan kecepatan terus meningkat hingga ke kecepatan keluar yang diperlukan, dan kecepatan setiap titik pada bagian tersebut adalah sama. Untuk profil plastik PVC dengan inti cetakan yang kompleks, inti cetakan diintegrasikan dengan pelat braket, ada yang dipasang pada pelat braket dengan menempatkan pin dan sekrup, dan ada pula yang tertanam pada pelat braket dengan tatahan yang rapat. Itu tidak dapat dengan mudah dibongkar saat digunakan, karena memakan waktu lama untuk memasang kembali dan melakukan debug. Shunt lelehan juga dilakukan dengan dua cara: pada kerucut shunt, dan pada bagian kompresi. Cetakan gradien bagian dapat digunakan sebagai cetakan profil utama. Cetakan ekstrusi profil plastik PVC adalah bagian inti dari lini produksi ekstrusi, yang meliputi cetakan mulut (juga dikenal sebagai kepala cetakan), cetakan pembentuk, tangki air pendingin, dll. Cetakan mulut dirakit dengan flensa pada kepala ekstruder dengan cara flensa, dan cincin pemanas, pelat pemanas, catu daya, dan termokopel terhubung. Cetakan pembentuk dan tangki air pendingin dipasang pada meja pembentuk dengan sekrup, dan pipa air serta pipa gas dihubungkan. Struktur dasar cetakan ekstrusi umumnya dirancang sebagai struktur beberapa templat yang ditumpuk dan dirakit. Oleh karena itu, saluran aliran seluruh die dibentuk dengan menghubungkan salah satu saluran aliran pada setiap bagian template, depan dan belakang. Pelat diposisikan dan diikat dengan pin dan baut untuk membentuk cetakan ekstrusi monolitik. Situasi dasarnya adalah: bagian aliran stabil dari cetakan ekstrusi sering kali terdiri dari pelat berlubang dan bagian depan leher, dan bagian depan dan paruh kedua leher juga dirancang sebagai dua templat, leher dan pelat transisi leher. Dimungkinkan juga untuk tidak menggunakan pelat berpori, tetapi merancang bagian depan saluran aliran leher menjadi saluran aliran silinder untuk menstabilkan aliran. Bagian belah cetakan ekstrusi dimulai dari paruh kedua leher dan meliputi kerucut belah, pelat braket belah, dan pelat susut. Pelat menyusut dapat dibagi tidak menjadi bekisting tunggal, tetapi bersama-sama dengan pelat yang telah dibentuk sebelumnya - bekisting. Bagian pembentuk cetakan ekstrusi melibatkan templat berikut: pelat rongga (juga dikenal sebagai pelat yang telah dibentuk sebelumnya), templat mulut (juga dikenal sebagai pelat pembentuk) dan inti (juga dikenal sebagai inti cetakan). Untuk cetakan profil yang lebih sederhana, pelat yang telah dibentuk sebelumnya digabungkan dengan templat mulut menjadi satu bekisting. 1. Poin-poin penting dari desain penampang produk Poin utama dari desain produk profil plastik PVC adalah ketebalan dan bentuk setiap bagian harus terdistribusi secara simetris, sehingga aliran material di kepala mesin seimbang, pendinginan dapat seragam. , dan tekanannya cenderung seimbang. Secara umum, ketebalan dinding maksimum dan ketebalan dinding minimum pada bagian yang sama berbeda < 50% is appropriate. If it is a part of a closed rib, the thickness of the rib should be 20% thinner than the wall thickness. In order to avoid the stress concentration at the corner of PVC plastic profile products, the shape change of the product should be smooth and smooth transition, generally the outer corner R is not less than 0.5mm, the inner corner R is not less than 0.25mm. The hollow part of the product should not be too small. The cross-sectional shape is preferably symmetrical. 2. Structure type and design principle of mold The mold is the forming part of the extruder, which is mainly composed of neck seat, shunt cone, support plate (also known as bracket), core mold, mouth template and adjusting screw. PVC plastic profile extrusion die county is mainly composed of three sections: feeding section one by machine base and distribution cone composed of machine head flow channel feeding section, is conical: melt distribution and forming section one by support plate and mouth die compression part constitute melt distribution and forming section, the shape is gradually close to the PVC plastic profile section, parallel section mouth die and core die constitute the machine head parallel section, (1) There are two types of mold structure for extruded plastic profiles: plate head and streamlined head. According to the different methods of processing and manufacturing the machine head, the streamlined head fork is divided into integral streamlined and segmented (also known as stepped) streamlined. (2) Mold design principle The mold is the key part of PVC plastic profile extrusion, and its function is to extrude a blank similar to the profile under the action of 10~25MPa extrusion force. PVC plastic profile mold runner design principle is that the runner section should be streamlined: there is enough compression ratio and shaped length to form a certain extrusion pressure: the flow resistance balance and flow symmetry of the cross-sectional gap of each runner part of the mold. The flow channel structure of the PVC plastic profile head is generally divided into three parts: feeding, compression (also known as transition part) and forming. Generally speaking, the length of the feed part of the long runner is 1 of the length of the shaping part. About 5~2 times, the length of the compression part is about 2~3 times the length of the shaping part. The maximum cross-sectional area of the compression section is in the outlet area of the bracket. The shape of the support ribs of the bracketer. The broad one is jujube nucleus-shaped. The thin ones are long prismatic. The shape of the divergence in the front of the scaffold is that it converges at the same angle on all sides, forming a torpedo body shape. The flow rate of molten material is different in the flow channel of feeding, compression and forming, the feeding part is the smallest, the forming part is the largest, and the transition part must be in between the two and gradually increase in the direction of extrusion. The melt flow rate is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the runner. The roughness of the runner in the head should be Ra0. 4~0.8ym, the roughness of the mouth mold runner of the stereotyped part is higher than the roughness of the inner runner, which should be Ra0.2~0. 4μm, When the extruded billet is just exported to the die, the size of the gap is increased than the mouth die, which is called the mold release expansion, that is, the Balas effect. This effect must be considered when the pulling speed of PVC plastic profile extrusion is slow and it is cooled near the outlet of the die mold. The release mold expansion of the outlet die is usually calculated by volume, and its expansion rate is generally 1.5~2.5 times, and this value changes with different aspects of melt temperature, pressure and velocity. The wall thickness size required for PVC plastic profiles depends on the wall thickness of the appropriate extruded billet on the one hand, and the pulling speed and extrusion amount on the other hand. The thickness of the extrusion blank wall mainly depends on the size of the mouth die gap, and then depends on the plasticizing performance of the material in the extruder, extrusion pressure, extrusion temperature, material performance and expansion value. First, the standard traction shrinkage rate for general wall thickness is ≤2.5%. The gap between the mouth die and the thickness of the product are taken (0.8~0.9) 1 1